 FUNDAMENTALS OF TAPPING FUNDAMENTALS OF TAPPING
Designed for PRECISION PROCESS EQUIPMENT Written by Mike Whitney and OSG Tap & Die Use the correct style of tap for the job 1. Hand style straight flute Chips stay in flute 2. Spiral point tap Pushes chip forward 3. Spiral flute (old style) Draws chips out 4. Spiral flute (new style) necked or din style Draws chips out 5. Spiral flute for aluminum Flute design draws chips out 6. Slow spiral for hard materials Draws chips out 7. Form tap No chips  Illustration of tap Terms Illustration of tap Terms
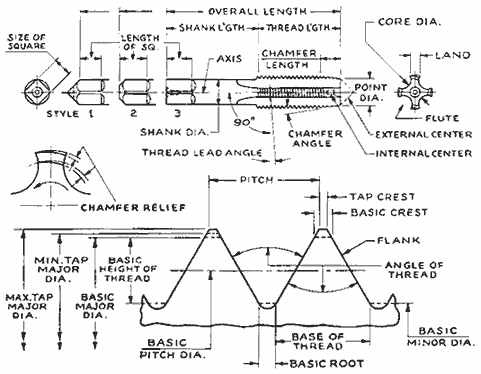
Pitch Diameter Limits Size 4-40 Tolerance .0958-.0991 (.0033) 2B fit GH2 3B fit GH2 Size 10-32 Tolerance .1697-.1736 (.0039) 2B fit GH3 3B fit GH2 Size 1/4-20 Tolerance .2175-.2224 (.0049) 2B fit GH5 3B fit GH3 Size 1/2-13 Tolerance .4565-.4500 (.0065) 2B fit GH5 3B fit GH5 Size 5/8-11 Tolerance .5660-5732 (.0072) Each H limit increases pitch diameter .0005 Example: for 1/4-20 tap using a GH5 limit the actual tap P.D. would be .220, right in the middle of the tolerance. A GH3 limit would be .219, only .0015 over low limit. Surface Treatments 1. Black Oxide/ Steam Oxide. A porous surface that retains cutting fluids to help add lubricity, reducing heat and friction. 2. Titanium Nitride (TiN). A hard (2000 vickers) durable surface coating (5 microns) that offers high lubricity (coef, of friction 0.4) increases tool life and also utilizes higher speeds and feeds than uncoated tools. 3. Titanium Carbonitride (TiCN). Harder than TiN (2,700 vickers) better for hard steels. Can also be used for aluminum and cast iron with good results. 4. Titanium Aluminum Nitride (TiALN). One of the hardest (2,800 vickers) with good lubricity (0.3 coef. of friction) of the standard coating. It also has the highest oxidation temperature (800 c) primarily used on carbide drills and end mills. Dry machining in the high speed applications is possible. 5. Diamond. The hardest of all coatings, (8,000 vickers) used in non ferrous applications, aluminum, copper, graphite, etc. There are usually two processes, pvd a lower cost coating and cvd which provides better grain structure, harder surfaces and up to four times longer tool life. Use the right OSG tap and coating for the material and application. Material Coating Low 1010 - High Carbon 1080, A36 Hot Roll. S/O, TIN, TICN Spiral Point, High Helix, Form tap* Cut 50 SFM Form 50 SFM Alloy Steels 41 - 4340, 8620, 1117 Etc. S/O, TiCN Spiral Point, High Helix, form Tap* Cut 25 SFM Form 20 SFM Tool Steels A2, D2, S7, H13 etc up to 35 HrC S/O, TICN Spiral Point and High Helix Cut 25 SFM Stainless Steels 300, 400 Series S/O, TiN, TICN Spiral Point, High Helix, Form Tap* FORM TAP Cut 25 SFM Form 25 SFM Nickel Alloys, Titanium, Inconel, PH Series S/O, TICN Spiral Point and Slow Spiral Flute 35 - 45 HrC 8 - 15 SFM cut only *FORM TAPS USUALLY 3/8 AND UNDER SLOW SPIRAL SLOW SPIRAL SPIRAL POINT HIGH HELIX If you don't remember anything else.......... You have to know this RPM = (3.82 x SFM) * SFM = 0.263 x RPM * IPM -= RPM X IPR * To calculate metric threads divide the pitch by 25.4 and multiply by RPM to give you IPM. Example: M8 x 1.25 @ 500 RPM 1.25/25.4=0.049x500=24.60 Tap Troubleshooting Tips 1. Use the correct style of tap for the job. 2. Use the largest minor diameter possible. Make sure the hole is clean, Do not over peck especially in stainless and nickel based materials. For best results use OSG cobalt and carbide drills for the best hole conditions. 3. Make sure you are using the correct GH Limit. 4. Surface treatments reduce friction and help prevent galling and tearing. 5. Be aware of the correct RPM range for the material you are tapping, too slow can cause as many problems as running too fast. 6. Chipping of spiral point taps is generally caused by RPM that is too slow. 7. Spiral flute taps are designed to eject the chip. RPM's that are too slow will cause chip packing and premature breakage. 8. Unless specifically required, 65% or less thread height is sufficient in most applications. A 65% thread is only 3% stronger than a 55% engagement. 9. Excessive depth does not equal extra strength. 2x dia. is a sufficient safety factor. 10. If none of the above works, Call us. 724-789-7853 Carbide Taps for all of your tapping needs. | 